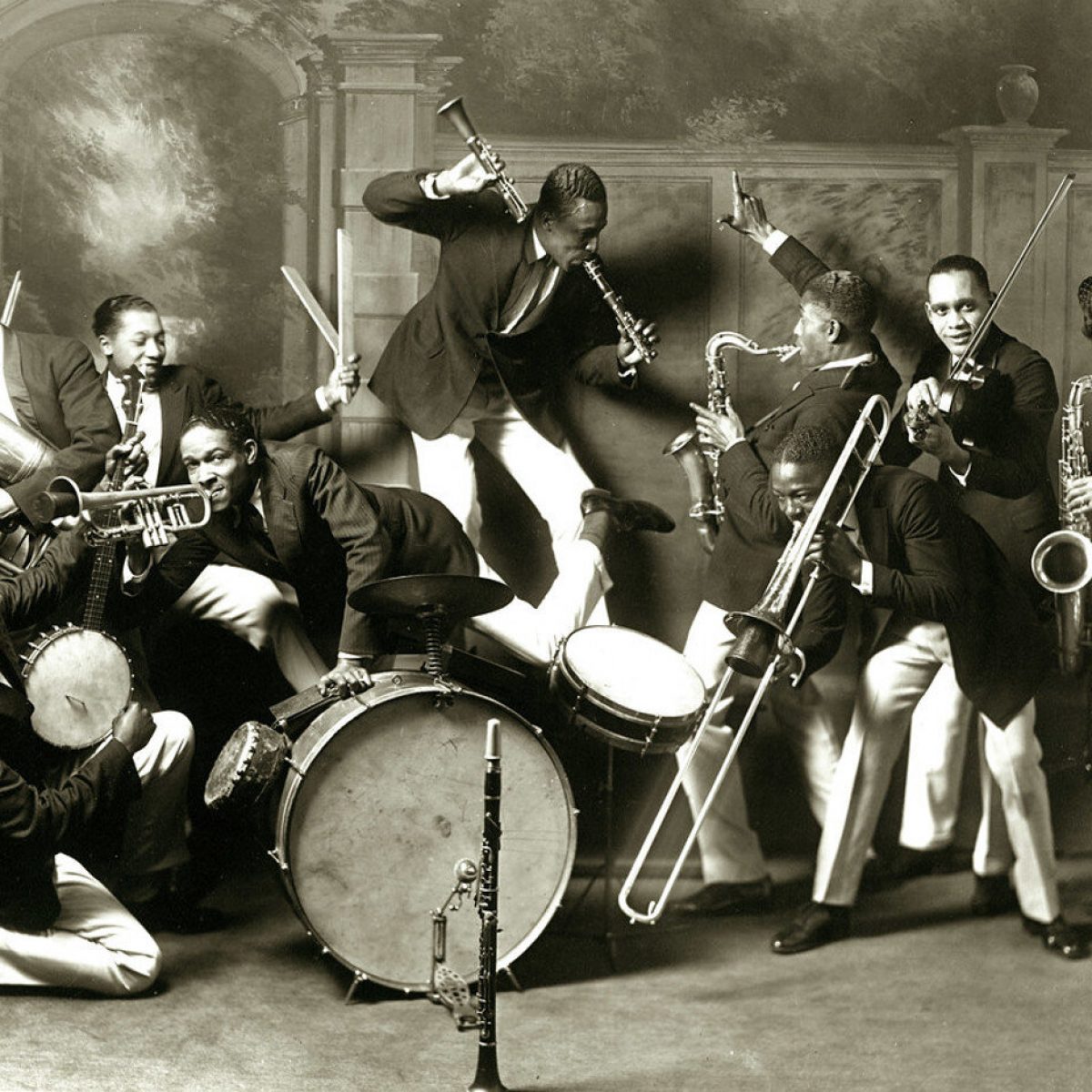
Formed in late 1923, the Wolverines, or Wolverine Orchestra, worked in clubs and dance halls in the Midwest for much of 1924, making occasional trips to a Gennett recording studio. It is best remembered today for including among its members the young Bix Beiderbecke, who after leaving the band became an influential jazz instrumentalist. Other members were pianist Dick Voynow, trombonist Al Gandee, tenor saxophonist George Johnson, clarinetist Jimmy Hartwell, banjoist Bob Gillette, tuba player Min Leibrook, and drummer Vic Moore.
Wolverine members obviously recognized that Beiderbecke was the band’s outstanding soloist–he is in the forefront on records. The others were competent on their respective instruments, at times elegant and imaginative. Few other bands at this time made records featuring so much improvisation. Yet the band was clearly well-rehearsed for sessions. Alternate takes of numbers establish that some musical ideas had been carefully worked out ahead of time.
The band recorded a total of fifteen titles for Gennett in 1924, thirteen of those titles with Beiderbecke. The last session with Beiderbecke was in early October. The Wolverines’ final session, with a young Jimmy McPartland on cornet, was on December 10, 1924. Later, Dick Voynow became in his own way important to the industry, and he used the name Original Wolverines for sessions in the late 1920s, leading different musicians than those of the original Wolverine Orchestra. Voynow had become “assistant director of the Brunswick recording laboratory of Chicago,” according to page 60 of the December 1929 issue of Talking Machine World & Radio-Music Merchant. (According to this article, Voynow in 1929 headed an eight-month tour throughout the South, recording hundreds of selections–not only Mexican but “hill billy [sic], French-Cajun, race, and popular”–on portable equipment. Page 27 of the September 1931 issue of Metronome states that he “is in charge” of the Chicago studio.)
Important influences on the band were the Original Dixieland Jazz Band (the Wolverines cut six numbers popularized a few years earlier by the Original Dixieland Jazz Band) and the New Orleans Rhythm Kings (the band covered some NORK tunes and even took its name from a NORK record issued by Gennett in June 1923, “Wolverine Blues“). The Wolverines were first to cut two numbers that would become jazz standards: “Copenhagen,” composed by Midwest bandleader Charlie Davis, and “Riverboat Shuffle,” composed for the band by a young Hoagy Carmichael, who was then a law student at Indiana University in Bloomington and a friend of the musicians. Voynow shared composer credit for “Riverboat Shuffle” since he arranged the new tune for recording purposes, thereby helping give it shape.
They also recorded some popular songs of 1924. Learning new material was more difficult for the Wolverines than for other bands of the era since these were not schooled musicians. Beiderbecke at this time could not read music. Philip R. Evans and Richard M. Sudhalter’s Bix: Man & Legend (New Rochelle, NY, and London: Quartet Books, 1974) reports that new tunes were learned by a slow method: Beiderbecke would play a few bars for other Wolverine members, repeating it often until members had a tune’s opening and closing.
The first of three references to the Wolverine Orchestra in Talking Machine World is in the July 1924 issue, which announces that “Oh Baby” backed by “Copenhagen” would be issued on Gennett 5453 in August.
Seven Wolverines discs with Beiderbecke were made by Gennett. Six discs were issued in Gennett’s normal 5000 series (three of these were announced in the trade journal, three were not). A seventh disc is Gennett 20062, which features “I Need Some Pettin’” and “Royal Garden Blues.”
Discs in Gennett’s 20000 series were presumably never available in shops since this was company’s “personal” series, the records being specially made for the individuals who ordered them. The Wolverines may have paid to have the two songs pressed (artists sometimes sold such records when playing in dance or concert halls). The label for Gennett 20062, probably pressed in July 1924, is the same in color and design as that of 5000 series Gennetts.

“Tiger Rag,” recorded at the same June 20 session as “I Need Some Pettin'” and “Royal Garden Blues,” was never issued. It exists on test pressings only, possibly only two or three existing. Frank Powers reports that surviving members of the Gennett family have one test pressing of “Tiger Rag.” It has a plain white label with the title and band’s name written in ink in long hand.
The first disc featured “Fidgety Feet” and “Jazz Me Blues,” two Original Dixieland Jazz Band numbers. They were issued on Gennett 5408, which normally would have been listed in “Advance Record Bulletins” of the May 1924 issue of Talking Machine World (Gennett 5406, featuring Vernon Dalhart on one side and Charles Harrison on the other, is announced in this issue, as are Gennett 5407, which features Bailey’s Lucky Seven and 5410, which features two polkas). Possibly the trade journal does not announce the Wolverines on Gennett 5408 because the record company did not issue the disc to its dealers nationwide, instead issuing it only to some Mid-West shops. It is a rare disc today.
Also missing from the trade journal’s lists of record releases is Gennett 5454: “Susie” backed by “Riverboat Shuffle.” The record number is only one after that given “Oh Baby” and “Copenhagen” (5453). The four songs were recorded during the band’s session of May 6, 1924. Gennett 5454 was probably available in Mid-West shops (and perhaps nowhere else) in August. The “Susie” that the Wolverines recorded was not the Harry Ruby-Bert Kalmar song popularized in 1922 by Eddie Cantor. It was a 1924 composition by Charlie Naset and Gus Kahn.
Gennett 5453–again, “Oh Baby” and “Copenhagen”–sold better than all other Wolverines discs though the Victor version of “Copenhagen” by the Benson Orchestra became the most popular recorded version of the 1920s. Cut on September 8, 1924–four months after the Wolverines recorded it–the Benson Orchestra’s version was issued on November 7, 1924. In January 1925, two other versions of “Copenhagen” were issued: Fletcher Henderson’s on Vocalion 14926 and Kitty Irvin’s on Gennett 5592.
The second reference to the Wolverine Orchestra in Talking Machine World is in the October 1924 issue, which announces the November release of “Sensation” and “Lazy Daddy” on Gennett 5542. It was another disc that couples two Original Dixieland Jazz Band compositions. The Wolverines cut the two numbers on September 16. Gennett announced the disc a mere month after the session and the two titles were issued on 5542 only six weeks after being recorded.
The third and final reference to the Wolverine Orchestra in the trade journal is in the November issue, which announced the December release of”Tia Juana” and “Big Boy” on Gennett 5565. Composers are cited after song titles. “Tia Juana” is credited to “Conley-Rodernick [sic],” which refers to Larry Conley and Gene Rodemich. Conley, a trombonist in Rodemich’s popular orchestra, composed many songs with Rodemich around this time. The new and unknown “Tia Juana” was a curious selection for the Wolverines’ session of October 6 (it was Beiderbecke’s last as a Wolverines member). Tom Griselle, musical director of Gennett’s New York studio, possibly anticipated that it would enjoy as much success as Rodemich and Conley’s “Easy Melody.”
Gene Rodemich and His Orchestra had recorded “Tia Juana” on June 10 for Brunswick 2680. That record was issued in November, so the Wolverines could not have known Rodemich’s recorded version when cutting their own in early October for Gennett. Orchestras at the time may have been playing it at dances. Hope Conley Lang, daughter of Larry Conley, reports that at least one stock band arrangement of “Tia Juana” was copyrighted by May 5, 1924. Jelly Roll Morton recorded “Tia Juana” a day before the Wolverines, on June 9–Gennett did not issue it (5632) until 1925. Emil Coleman and His Club Trocadero Orchestra recorded it for Vocalion in late August, 1924. It was issued as Vocalion 14879 in November–too late for the record to have influenced the Wolverines.
The selection of “Big Boy” for the session in early October (Brian Rust states October 7 but other sources state October 8) is not surprising given the song’s genuine popularity at the time. Nearly a dozen versions were available by the time Gennett 5565 was issued in December 1924.
“Big Boy” features a tour de force performance by Beiderbecke, who provides a lead melody on cornet in the opening; follows the saxophonist’s solo with a chorus improvised on piano, playing without band accompaniment (the Wolverines’ regular pianist was never so prominent on a record–it was the first time Beiderbecke recorded as a pianist); and finally contributes to spirited ensemble playing at the close, his distinctive cornet heard only seconds after his piano solo ends. “Big Boy” was composed by Milton Ager. Jack Yellen provided lyrics to the song but no Wolverines records feature vocals.
The band’s earliest sessions had been in Gennett’s studio in Richmond, Indiana, but the last three sessions (two with Beiderbecke, one without) were in Gennett’s New York studio on East 37th Street. The band had traveled eastward for an engagement at a popular dance hall, an event noted on page 70 of the October 1924 issue of Metronome: “The Wolverines came to New York and opened at the Cinderella [Ballroom], where they were one of the biggest hits that ever hit New York. The Wolverines, under the direction of Richard Voynow, have been the favorite orchestra of all the college and fraternity houses throughout Ohio, Indiana, Kentucky and Michigan…”
Tom Griselle supervised the New York City sessions. According to the March 1924 issue of Talking Machine World, Griselle had taken a year’s absence (Frederick Woods had served as musical director since September 1923) and was by March of 1924 “again in charge of the Gennett record-making activities of the Starr Piano Co. in the New York laboratories.”
The name “Bix” appears for the first time in Talking Machine World in the December 1924 issue. Gennett 5569 is listed as scheduled for release in January 1925. This disc features the Sioux City Six performing “I’m Glad” and “Flock o’ Blues,” which had been recorded on October 11. Gennett credits the disc to “Sioux City Six Featuring Bix and Miff Moe [sic].” Miff Mole was a trombonist who recorded prolifically. This marked the beginning of Beiderbecke’s recording career without the Wolverines–he was still an obscure musician, his departure from the Midwest band attracting no notice at the time.
Talking Machine World never featured articles about Beiderbecke though Charles Burnette Beiderbecke is mentioned in an article titled “Music Dept. Changes Hands.” Dated July 2, 1924, the article reports that “C.B. Beiderbeck [sic]” of Davenport, Iowa, had just bought the talking machine department at the Harned & Von Maur store. Charles, who was 28 years old at this time, was an older brother who had, five years earlier (after the Armistice), brought into the Beiderbecke household an Original Dixieland Jazz Band disc featuring “Tiger Rag” and “Skeleton Jangle.” The disc inspired the young Bix to practice his music. Evans and Sudhalter’s Bix: Man & Legend gives an account of him slowing the phonograph turntable as the record played so he could learn the notes on a nearby piano. Since Charles in 1924 operated his own talking machine department in Davenport, beginning in the months that Wolverines discs were being issued by Gennett, it is likely that Charles stocked his younger brother’s records.
By Tim Gracyk from his book “Popular American Recording Pioneers 1895 -1925.”
| Title | Recording Date | Recording Location | Company |
| Big Boy (Milton Ager / Jack Yellen) |
10-7-1924 | New York, New York | Gennett 5565-B |
| Copenhagen (Charlie Davis / Walter Melrose) |
5-6-1924 | Richmond, Indiana | Gennett 5453-B Claxtonola 40336-B |
| Fidgety Feet (Nick LaRocca / Larry Shields) |
2-18-1924 | Richmond, Indiana | Gennett 5408-A |
| I Need Some Pettin’ (R. King / Ted Fiorito / Gus Kahn) |
7-20-1924 | Richmond, Indiana | Gennett 20062-A |
| Jazz Me Blues (Tom Delaney) |
2-18-1924 | Richmond, Indiana | Gennett 5408-B |
| Lazy Daddy (Nick LaRocca / Larry Shields / Henry Ragas) |
9-16-1924 | New York, New York | Gennett 5542-B 9080-A |
| Lazy Daddy (Nick LaRocca / Larry Shields / Henry Ragas) |
9-16-1924 | New York, New York | Gennett 5542-B 9080-B |
| Oh Baby (Walter Donaldson / Buddy DeSylva) |
5-6-1924 | Richmond, Indiana | Gennett 5453-A |
| Prince Of Wails (Elmer Schoebel) |
12-5-1924 | New York, New York | Gennett 5620-A |
| Riverboat Shuffle (Hoagy Carmichael) |
5-6-1924 | Richmond, Indiana | Gennett 5454-A |
| Royal Garden Blues (Clarence Williams / Spencer Williams) |
7-20-1924 | Richmond, Indiana | Gennett 20062-B |
| Sensation (Eddie Edwards) |
9-16-1924 | New York, New York | Gennett 5542-A Claxtonola 40375-A |
| Susie (Of The Islands) (C. Naser / Gus Kahn) |
5-6-1924 | Richmond, Indiana | Gennett 5454-B 11855-A |
| Susie (Of The Islands) (C. Naser / Gus Kahn) |
5-6-1924 | Richmond, Indiana | Gennett 5454-B 11855-B |
| Tia Juana (Larry Conley / Gene Rodemich) |
10-7-1924 | New York, New York | Gennett 5565-A |
| Tiger Rag (Nick LaRocca) |
7-20-1924 | Richmond, Indiana | Hot Record Society 24 |
| When Sugar Walks Down The Street Vocal Chorus, Dave Harman (Gene Austin / Jimmy McHugh) |
12-5-1924 | New York, New York | Gennett 5620-B |
| Artist | Instrument |
| Bix Beiderbecke | Cornet, Piano |
| George Brunnies | Trombone, Kazoo |
| Al Gandee | Trombone |
| Bob Gillette | Banjo |
| Dave Harman | Vocals |
| Jimmy Hartwell | Clarinet, Alto Saxophone |
| George Johnson | Tenor Saxophone |
| Min Leibrook | Bass |
| Vic Moore | Drums |
| Jimmy McPartland | Cornet |
| Dick Voynow | Piano, Leader |
| Bix: Man And Legend, by Richard M. Sudhalterr and Philip R. Evans, Arlington House Publishers, 1974 |
| Remembering Bix, by Ralph Berton, Harper & Row, 1974 |
| Bix Beiderbecke by Burnett James, Cassell & Co, Ltd., 1959 |
| The Stardust Road by Hoagy Carmichael, University of Indiana Press, 1946 |
Redhotjazz.com was a pioneering website during the "Information wants to be Free" era of the 1990s. In that spirit we are recovering the lost data from the now defunct site and sharing it with you.
Most of the music in the archive is in the form of MP3s hosted on Archive.org or the French servers of Jazz-on-line.com where this music is all in the public domain.
Files unavailable from those sources we host ourselves. They were made from original 78 RPM records in the hands of private collectors in the 1990s who contributed to the original redhotjazz.com. They were hosted as .ra files originally and we have converted them into the more modern MP3 format. They are of inferior quality to what is available commercially and are intended for reference purposes only. In some cases a Real Audio (.ra) file from Archive.org will download. Don't be scared! Those files will play in many music programs, but not Windows Media Player.






