![]()
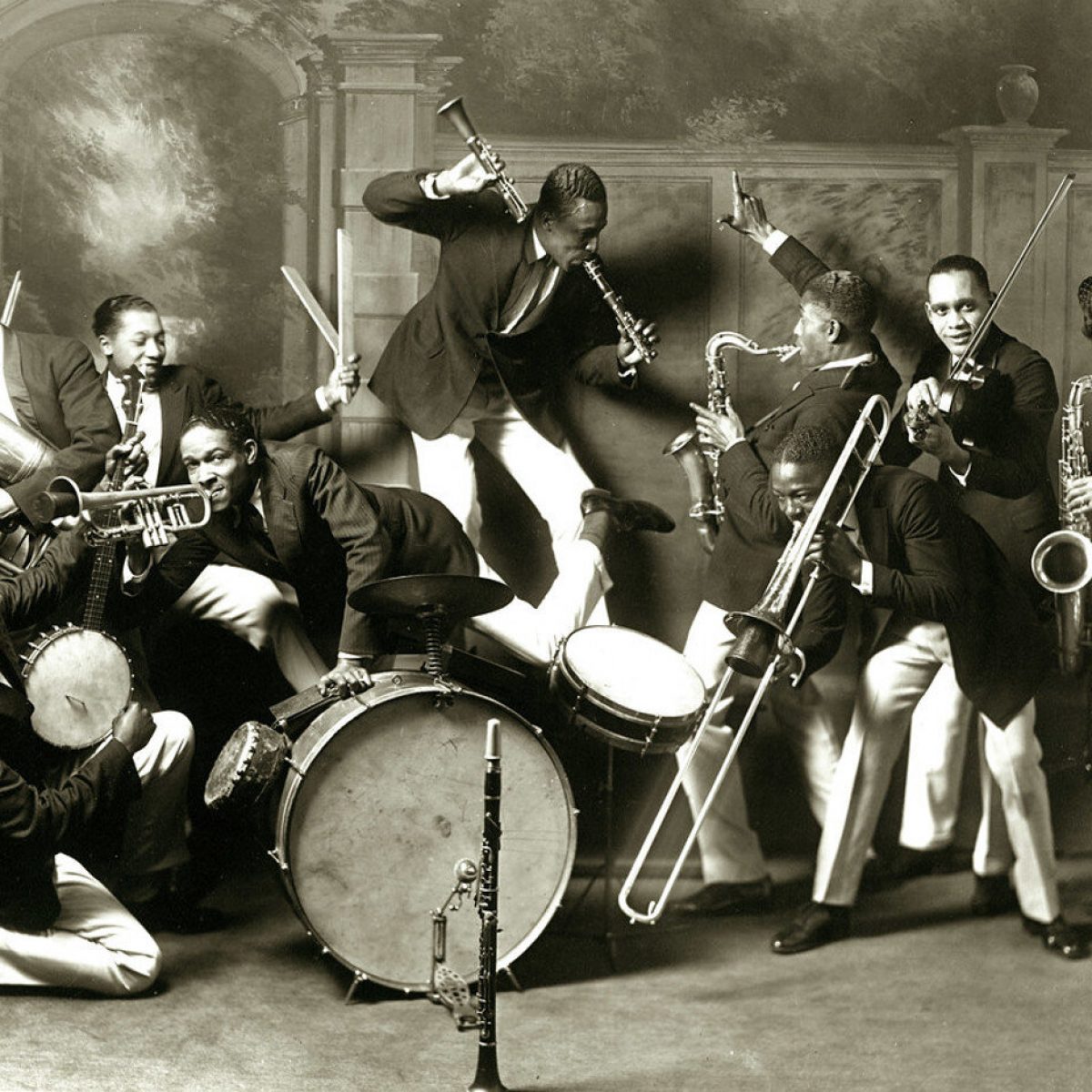
 Louis Armstrong was the greatest of all Jazz musicians. Armstrong defined what it was to play Jazz. His amazing technical abilities, the joy and spontaneity, and amazingly quick, inventive musical mind still dominate Jazz to this day. Only Charlie Parker comes close to having as much influence on the history of Jazz as Louis Armstrong did.
Louis Armstrong was the greatest of all Jazz musicians. Armstrong defined what it was to play Jazz. His amazing technical abilities, the joy and spontaneity, and amazingly quick, inventive musical mind still dominate Jazz to this day. Only Charlie Parker comes close to having as much influence on the history of Jazz as Louis Armstrong did.
Like almost all early Jazz musicians, Louis was from New Orleans. He was from a very poor family and was sent to reform school when he was twelve after firing a gun in the air on New Year’s Eve. At the school he learned to play cornet.
After being released at age fourteen, he worked selling papers, unloading boats, and selling coal from a cart. He didn’t own an instrument at this time, but continued to listen to bands at clubs like the Funky Butt Hall. Joe “King” Oliver was his favorite and the older man acted as a father to Louis, even giving him his first real cornet, and instructing him on the instrument. By 1917 he played in an Oliver inspired group at dive bars in New Orleans’ Storyville section.
In 1919 he left New Orleans for the first time to join Fate Marable’s band in St. Louis. Marable led a band that played on the Strekfus Mississsippi river boat lines. When the boats left from New Orleans Armstrong also played regular gigs in Kid Ory‘s band. Louis stayed with Marable until 1921 when he returned to New Orleans and played in Zutty Singleton’s. He also played in parades with the Allen Brass Band, and on the bandstand with Papa Celestin’s Tuxedo Orchestra , and the Silver Leaf Band.
 When King Oliver left the city in 1919 to go to Chicago, Louis took his place in Kid Ory’s band from time to time. In 1922 Louis received a telegram from his mentor Joe Oliver, asking him to join his Creole Jazz Band at Lincoln Gardens (459 East 31st Street) in Chicago.
When King Oliver left the city in 1919 to go to Chicago, Louis took his place in Kid Ory’s band from time to time. In 1922 Louis received a telegram from his mentor Joe Oliver, asking him to join his Creole Jazz Band at Lincoln Gardens (459 East 31st Street) in Chicago.
This was a dream come true for Armstrong and his amazing playing in the band soon made him a sensation among other musicians in Chicago. The New Orleans style of music took the town by storm and soon many other bands from down south made their way north to Chicago.
While playing in Oliver’s Creole Jazz Band, Armstrong met Lillian Hardin, a piano player and arranger for the band. In February of 1924 they were married. Lil was a very intelligent and ambitious woman who felt that Louis was wasting himself playing in Oliver’s band. By the end of 1924 she pressured Armstrong to reluctantly leave his mentor’s band.
He briefly worked with Ollie Powers’ Harmony Syncopators before he moved to New York to play in Fletcher Henderson’s Orchestra for 13 months. During that time he also did dozens of recording sessions with numerous Blues singers, including Bessie Smith’s 1925 classic recording of “St. Louis Blues“. He also recorded with Clarence Williams and the Red Onion Jazz Babies.
In 1925 Armstrong moved back to Chicago and joined his wife’s band at the Dreamland Cafe (3520 South State Street). He also played in Erskine Tate’s Vendome Orchestra and then with Carrol Dickenson’s Orchestra at the Sunset Cafe (313-17 East 35th Street at the corner of Calmet Street). Armstrong recorded his first Hot Five records that same year.
This was the first time that Armstrong had made records under his own name. The records made by Louis Armstrong’s Hot Five and Hot Seven are considered to be absolute jazz classics and the peak of Armstrong’s creative powers. The band never played live, but continued recording until 1928.
While working at the Sunset, Louis met his future manager, Joe Glaser. Glaser managed the Sunset at that time. Armstrong continued to play in Carrol Dickenson’s Orchestra until 1929. He also led his own band on the same venue under the name of Louis Armstrong and his Stompers. For the next two years Armstrong played with Carroll Dickerson’s Savoy Orchestra and with Clarence Jones’ Orchestra in Chicago.
By 1929 Louis was becoming a very big star. He toured with the show “Hot Chocolates” and appeared occasionally with the Luis Russell Orchestra, with Dave Peyton, and with Fletcher Henderson. Armstrong moved to Los Angeles in 1930 where he fronted a band called Louis Armstrong and his Sebastian New Cotton Club Orchestra. In 1931 he returned to Chicago and assembled his own band for touring purposes. In June of that year he returned to New Orleans for the first time since he left in 1922 to join King Oliver’s Creole Jazz Band.
Armstrong was greeted as a hero, but racism marred his return when a White radio announcer refused to mention Armstrong on the air and a free concert that Louis was going to give to the cities’ African-American population was cancelled at the last minute. Louis and Lil also separated in 1931.
In 1932 he returned to California, before leaving for England where he was a great success. For the next three years Armstrong was almost always on the road. He crisscrossed the U.S. dozens of times and returned to Europe playing in Denmark, Sweden, Norway, Holland and England. In 1935 he returned to the U.S. and hired Joe Glaser to be his manager.
He had known Glaser when he was the manager of the Sunset Cafe in Chicago in the 1920s. Glaser was allegedly connected to the Al Capone mob, but proved to be a great manager and friend for Louis. Glaser remained Armstrong’s manager until his death in 1969.
Glaser took care of the business end of things, leaving Armstrong free to concentrate on his music. He also hired the Luis Russell Orchestra as Louis’ backup band with Russell as the musical director. This was like going home for Armstrong, because Russell’s Orchestra was made up of predominantly New Orleans musicians, many of whom had also played with King Oliver.
The band was renamed Louis Armstrong and his Orchestra and was one of the most popular acts of the Swing era. Glaser put the band to work and they toured constantly for the next ten years. During this period Armstrong became one of the most famous men in America.
In 1938 Lil and Louis finally got a divorce. Louis then married Alpha, his third wife. The endless touring was hard on their marriage and they were divorced four years later, but Armstrong quickly remarried Lucille and they remained married for the rest of his life.
For the next nine years the Louis Armstrong Orchestra continued to tour and release records, but as the 1940s drew to a close the public’s taste in Jazz began to shift away from the commercial sounds of the Swing era and big band Jazz. The so-called Dixieland Jazz revival was just beginning and Be Bop was also starting to challenge the status quo in the Jazz world. The Louis Armstrong Orchestra was beginning to look tired and concert and record sales were declining. Critics complained that Armstrong was becoming too commercial.
So, in 1947 Glaser fired the orchestra and replaced them with a small group that became one of the greatest and most popular bands in Jazz history. The group was called the Louis Armstrong Allstars and over the years featured exceptional musicians like Barney Bigard, Jack Teagarden, Sidney ‘Big Sid’ Catlett , vocalist Vilma Middleton, and Earl Hines.
The band went through a number of personnel changes over the years but remained extremely popular worldwide. They toured extensively travelling to Africa, Asia, Europe and South America for the next twenty years until Louis’ failing health caused them to disband. Armstrong became known as America’s Ambassador.
In 1963 Armstrong scored a huge international hit with his version of “Hello Dolly”. This number one single even knocked the Beatles off the top of the charts. In 1968 he recorded another number one hit with the touchingly optimistic “What A Wonderful World”. Armstrong’s health began to fail him and he was hospitalized several times over the remaining three years of his life, but he continued playing and recording. On July 6th 1971 the world’s greatest Jazz musician died in his sleep at his home in Queens, New York.
Thanks to Mary Devito for her help with this page.
| Louis Armstrong and his Hot Five | Louis Armstrong and his Hot Seven |
| Louis Armstrong and his Orchestra | Louis Armstrong and his Savoy Ballroom Five |
| Louis Armstrong and his Stompers | Louis Armstrong and his Sebastian New Cotton Club Orchestra |
| Louis Armstrong with the Polynesians | Louis Armstrong With Andy Iona And His Islanders |
| Louis Armstrong and the Mills Brothers | Louis Armstrong With Jimmy Dorsey and his Orchestra |
| Title | Recording Date | Recording Location | Company |
| Elder Eatmore’s Sermon On Generosity (Rogers) |
8-11-1938 | New York, New York | Decca 15043 Decca 29231 |
| Elder Eatmore’s Sermon On Throwing Stones (Rogers) |
8-11-1938 | New York, New York | Decca 15043 Decca 29231 |
| Title | Director | Year |
| Ex-Flame | Victor Halperin | 1930 |
| I’ll Be Glad When You’re Dead You Rascal You | Dave Fleischer | 1930 |
| A Rhapsody in Black and Blue | Aubrey Scotto | 1932 |
| Pennies from Heaven | Norman Z. McLeod | 1936 |
| Artists & Models | Raoul Walsh | 1937 |
| Every Day’s a Holiday | A. Edward Sutherland | 1937 |
| Dr. Rhythm | Frank Tuttle | 1938 |
| Going Places | Ray Enright | 1938 |
| Cabin In The Sky | Vincente Minnelli & Busby Berkeley | 1943 |
| Show Business at War | Louis De Rochemont | 1943 |
| Jam Session | Charles Barton | 1944 |
| Atlantic City | Ray McCarey | 1944 |
| Pillow to Post | Vincent Sherman | 1945 |
| New Orleans | Arthur Lubin | 1947 |
| A Song Is Born | Howard Hawks | 1948 |
| Botta e risposta | Mario Soldati | 1949 |
| Young Man with a Horn | Michael Curtiz | 1950 |
| Here Comes the Groom | Frank Capra | 1951 |
| The Strip | László Kardos | 1951 |
| Glory Alley | Raoul Walsh | 1952 |
| The Glenn Miller Story | Anthony Mann | 1953 |
| High Society | Charles Walters | 1956 |
| Satchmo the Great | 1957 | |
| Die Nacht vor der Premiere | Georg Jacoby | 1959 |
| The Beat Generation | Charles F. Haas | 1959 |
| La Paloma | Paul Martin | 1959 |
| Kćrlighedens melodi | Bent Christensen | 1959 |
| Jazz On A Summer’s Day | Bert Stern | 1959 |
| The Five Pennies | Melville Shavelson | 1959 |
| The Five Pennies | Melville Shavelson | 1959 |
| Paris Blues | Martin Ritt | 1961 |
| Auf Wiedersehen | Harald Philipp | 1961 |
| When the Boys Meet the Girls | Alvin Ganzer | 1965 |
| A Man Called Adam | Leo Penn | 1966 |
| Hello, Dolly! | Gene Kelly | 1969 |
| On the Road with Duke Ellington | Robert Drew | 1974 |
| My Life in New Orleans by Louis Armstrong, Da Capo Press, 1954 Swing That Music by Louis Armstrong, Da Capo Press, 1936 Louis Armstrong by Hughes Panassie Da Capo Press, 1971 Louis by Max Jones & John Clinton, Da Capo Press, 1971 Louis Armstrong : An Extravagant Life by Laurence Bergreen, Broadway Books, 1997 Louis Armstrong’s New Orleans by Thomas Brothers, W.W. Norton and Company, 2006 |
Redhotjazz.com was a pioneering website during the "Information wants to be Free" era of the 1990s. In that spirit we are recovering the lost data from the now defunct site and sharing it with you.
Most of the music in the archive is in the form of MP3s hosted on Archive.org or the French servers of Jazz-on-line.com where this music is all in the public domain.
Files unavailable from those sources we host ourselves. They were made from original 78 RPM records in the hands of private collectors in the 1990s who contributed to the original redhotjazz.com. They were hosted as .ra files originally and we have converted them into the more modern MP3 format. They are of inferior quality to what is available commercially and are intended for reference purposes only. In some cases a Real Audio (.ra) file from Archive.org will download. Don't be scared! Those files will play in many music programs, but not Windows Media Player.






